Publications
Original Research
- Santiago-Fernández O, Coletto L, Tasset I, Kaushik S, Concepcion AR, Qaisar R, Macho-González A, Lindenau K, Diaz A, Khawaja RR, Donega S, Banskota N, Ubaida-Mohien C, Pharaoh G, Ahn B, Hartnell LM, Ramírez-Pardo I, Chavda B, Gazteluiturri A, Kinter M, Ferrucci L, Reisz JA, D’Alessandro A, Van Remmen H, Muñoz-Cánoves P, Feske S, Cuervo AM. Age-related decline of chaperone-mediated autophagy in skeletal muscle leads to progressive myopathy. Nat Metab. 2025 Dec 3. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01412-9.
- Erdogmus S*, Concepcion AR*, Sidhu I, Tao AY, Li W, Rocha PP, Huang B, Garippa R, Lee B, Lee A, Hell JW, Lewis RS, Prakriya M, Feske S. Cavβ1 regulates T cell expansion and apoptosis independently of voltage-gated Ca2+ channel function. Nat Commun. 2022. doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29725-3. Epub 2022 Apr 19. *Equal contribution.
- Concepcion AR, Wagner II LE, Zhu J, Tao AY, Yang J, Khodadadi-Jamayran A, Wang Y, Liu M, Rose RE, Jones DR, Coetzee WA, Yule DI, Feske S. The volume regulated anion channel LRRC8C suppresses T cell function by regulating cyclic dinucleotide transport and STING-p53 signaling. Nat Immunol. 2022 Feb;23(2):287-302. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-01105-x. Epub 2022 Feb 1.
- Kahlfuss S, Kaufmann U, Concepcion AR, Noyer L, Raphael D, Vaeth M, Yang J, Pancholi P, Maus M, Muller J, Kozhaya L, Khodadadi-Jamayran A, Sun Z, Shaw P, Unutmaz D, Stathopulos PB, Feist C, Cameron SB, Turvey SE, Feske S. STIM1-mediated calcium influx controls antifungal immunity and the metabolic function of non-pathogenic Th17 cells. EMBO Mol Med. 2020 Aug 7;12(8):e11592. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201911592. Epub 2020 Jul 1.
- Aulestia FJ, Groeling J, Bomfim GHS, Costiniti V, Manikandan V, Chaloemtoem A, Concepcion AR, Li Y, Wagner II LE, Idaghdour Y, Yule DI, Lacruz RS. Fluoride exposure alters Ca2+ signaling and mitochondrial function in enamel cells. Sci Signal. 2020 Feb 18;13(619):eaay0086. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aay0086.
- Celay J, Lozano T, Concepcion AR, Beltrán E, Rudilla F, García-Barchino MJ, Robles EF, Rabal O, De Miguel I, Panizo C, Casares N, Oyarzabal J, Medina JF, Lasarte JJ, Martínez-Climent JA. Targeting the anion exchanger AE2 with specific peptides as a new therapeutic approach in B lymphoid neoplasms. Haematologica. 2018 Jun;103(6):1065-1072. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.175687.
- Concepcion AR, Vaeth M, Wagner II LE, Eckstein M, Hecht L, Yang J, Crottes D, Seidl M, Shin HP, Weidinger C, Cameron S, Turvey SE, Issekutz T, Meyts I, Lacruz RS, Cuk M, Yule DI, Feske S. Store-operated Ca2+ entry regulates Ca2+-activated chloride channels and eccrine sweat gland function. J Clin Invest. 2016 Nov 1;126(11):4303-4318. doi: 10.1172/JCI89056.
- Nurbaeva MK, Eckstein M, Concepcion AR, Smith CE, Srikanth S, Paine ML, Gwack Y, Hubbard MJ, Feske S, Lacruz RS. Dental enamel cells express functional SOCE channels. Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 30;5:15803. doi: 10.1038/srep15803.
- Concepcion AR, Salas JT, Sáez E, Sarvide S, Ferrer A, Portu A, Uriarte I, Hervás-Stubbs S, Oude Elferink RP, Prieto J, Medina JF. CD8+ T cells undergo activation and programmed death-1 repression in the liver of aged Ae2a,b–/– mice favoring autoimmune cholangitis. Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 6;6(30):28588-606. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5665.
- Munoz-Garrido P, Marin JJ, Perugorria MJ, Urribarri AD, Erice O, Sáez E, Uriz M, Sarvide S, Portu A, Concepcion AR, Romero MR, Monte MJ, Santos-Laso A, Hijona E, Jimenez-Agüero R, Marzioni M, Beuers U, Masyuk TV, LaRusso NF, Prieto J, Bujanda L, Drenth JP1, Banales JM. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Inhibits Hepatic Cystogenesis in Experimental Models of Polycystic Liver Disease. J Hepatol. 2015 Oct;63(4):952-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.023.
- Vaeth M, Zee I, Concepcion AR, Maus M, Shaw P, Portal-Celhay C, Zahra A, Kozhaya L, Weidinger C, Philips J, Unutmaz D, Feske S. Ca2+ signaling but not Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry is required for the function of macrophages and dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2015 Aug 1;195(3):1202-17. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403013.
- Concepcion AR, Salas JT, Sarvide S, Sáez E, Ferrer A, López M, Portu A, Banales JM, Hervás-Stubbs S, Oude Elferink RPJ, Prieto J, Medina JF. Anion exchanger 2 is critical for CD8+ T cells to maintain pHi homeostasis and modulate immune responses. Eur J Immunol. 2014 May;44(5):1341-51. doi:10.1002/eji.201344218.
- Uriarte I, Fernandez-Barrena MG, Monte MJ, Latasa MU, Chang HC, Carotti S, Vespasiani-Gentilucci U, Morini S, Vicente E, Concepcion AR, Medina JF, Marin JJ, Berasain C, Prieto J, Avila MA. Identification of fibroblast growth factor 15 as a novel mediator of liver regeneration and its application in the prevention of post-resection liver failure in mice. Gut. 2013 Jun;62(6):899-910. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302945.
Pre-prints
- Remark J, Tong J, Lin MJ, Concepcion AR, Mareedu S, Babu GJ, Feske S, Lu CP. Neurotransmitter signaling specifies sweat gland stem cell fate through SLN-mediated intracellular calcium regulation. bioRxiv.. 2023. Sep 13:2023.09.10.557066. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.10.557066.
Book Chapters
- Granados ST, Yanushkevich S, Lok J, Concepcion AR. Analysis of Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry in Primary T Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2025. 2025:2904:91-113. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4414-0_7
Reviews
- Yanushkevich S, Zieminska A, Gonzalez J, Añazco F, Song R, Arias-Cavieres A, Granados ST, Zou J, Rao Y, Concepcion AR. Recent advances in the structure, function, and regulation of the volume-regulated anion channels and their role in immunity. J Physiol. 2024 Dec 22. doi: 10.1113/JP285200.
- Feske S, Concepcion AR, Coetzee WA. Eye on ion channels in immune cells. Sci Signal. 2019 Mar 12;12(572). pii: eaaw8014. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaw8014.
- Concepcion AR, Feske S. Regulation of epithelial ion transport in exocrine glands by store-operated Ca2+ entry. Cell Calcium. 2017 May;63:53-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2016.12.004.
- Concepcion AR, J, Medina JF. Mouse models of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. 21(18):2401-13. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150316121622.
- Concepcion AR, Lopez M, Ardura-Fabregat A, Medina JF. Role of AE2 for pHi regulation in biliary epithelial cells. Front Physiol. 2014 Jan, Volume 4, Article 413:1-7. doi:10.3389/fphys.2013.00413.
- Concepcion AR, Medina JF. Approaches to the pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis through animal models. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2012 Feb;36(1):21-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2011.07.007.
Commentaries about our work
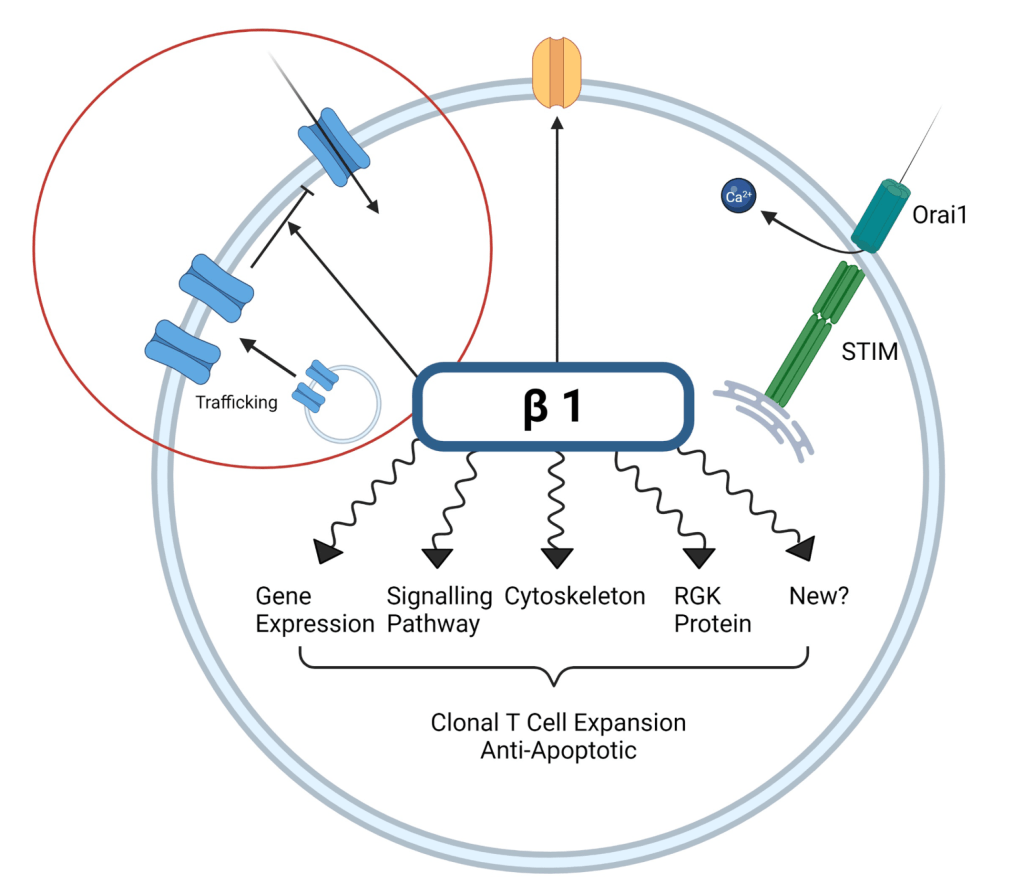
Evidence of absence with a twist: voltage-operated Ca2+ channel β subunit in T cells
By Jemma Strauss & Anant B. Parekh. Cell Calcium, 2022.
New roles for the β1 subunit in regulating T cells. In excitable cells, β regulates trafficking and gating of voltage-operated Ca2+ channels (VOCCs). The new work by Feske, Prakriya et al. now unequivocally rule out functional VOCCs in murine and human T cells. The major route for Ca2+ entry is through Orai1, activated by the ER-resident STIM proteins. Roles for β subunit independent of VOCC regulation include control of other ion channels, as well as a host of intracellular mechanisms that might be connected.
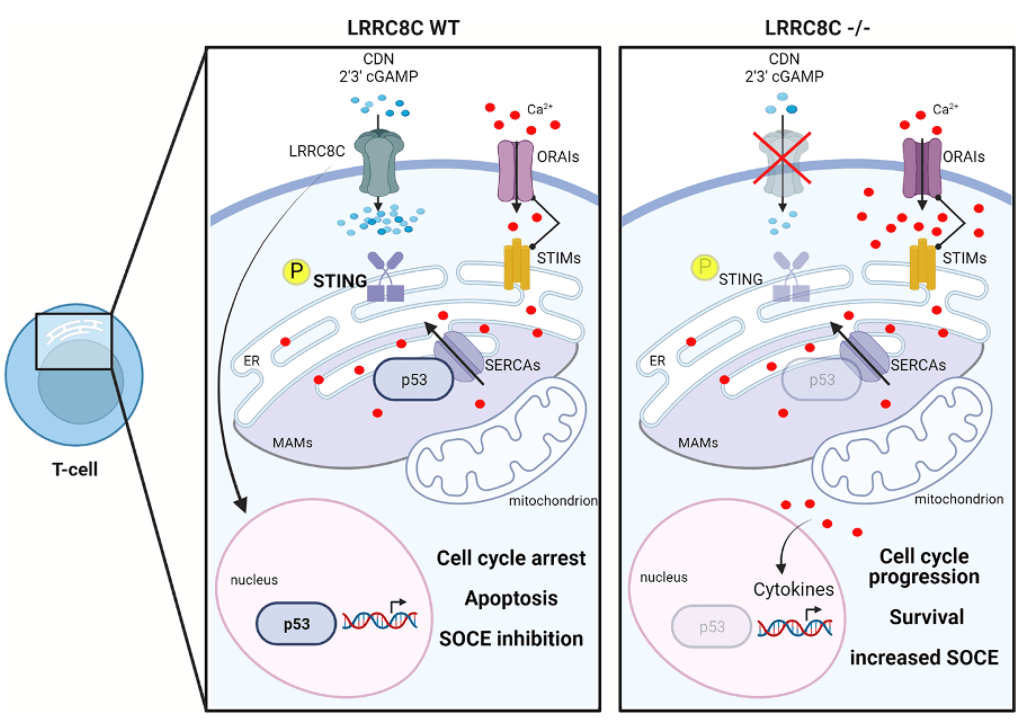
The LRRC8C-STING-p53 axis in T cells: A Ca2+ affair
By Sonia Missiroli, Carlotta Giorgi & Paolo Pinton. Cell Calcium, 2022.
Up to now, no role has been associated with VRAC channels in T cells. In a recent paper published in Nature Immunology, LRRC8C has been described as an essential component of VRAC in T cells. These data raise the intriguing possibility that the LRRC8C-STING-p53 signaling axis may represent a new inhibitory pathway in T cells that controls their function and adaptive immunity.

Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel proteins do not function as ion channels in T cells
By Michael D. Cahalan. Science Signaling, 2022.
Calcium (Ca2+) signaling has long been known to be crucial for T cell activation. Erdogmus et al. tested the function of voltage-gated Ca2+ channel (CaV) proteins and discovered a nonchannel function mediated by an accessory subunit but found no evidence for CaV channel activity in T cells.

An anion channel for cyclic dinucleotides in T cells
By Jiachen Chu & Zhaozhu Qiu. Nature Immunology, 2022.
LRRC8C is an essential component of volume-regulated anion channel (VRAC) in T cells. By mediating the transport of cGAMP, LRRC8C inhibits T cell function by activating STING and the tumor suppressor p53.
By John F. Foley. Science Signaling, 2022.
The cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP taken up through the anion channel component LRRC8C suppresses T cell function.
